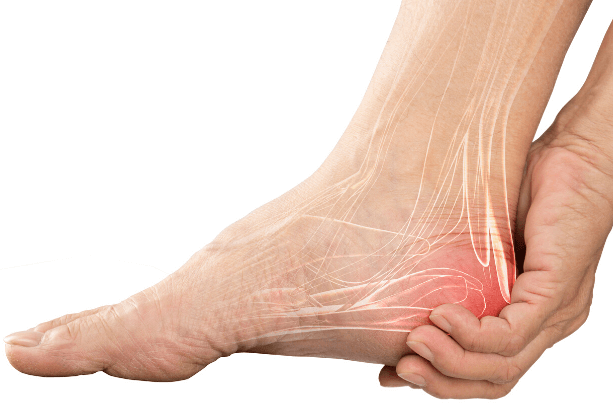
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot and connects the heel bone to the toes. It is one of the most frequent causes of heel pain, affecting athletes, runners, and individuals who spend a lot of time on their feet.
Biomechanical Assessment
A thorough biomechanical assessment is essential for diagnosing plantar fasciitis and tailoring an effective treatment plan. This assessment typically includes:
1. Gait Analysis: Observing the patient's walking pattern to identify any abnormalities. For instance, overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot) can strain the plantar fascia. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, gait analysis can help identify specific biomechanical patterns contributing to plantar fasciitis.
2. Foot Structure Evaluation: Assessing the foot's arch (high, normal, or flat) and identifying any structural deformities or imbalances. Research in the Journal of Foot and Ankle Research highlights the importance of evaluating foot arch height, as abnormal arches can significantly impact plantar fascia strain.
3. Range of Motion (ROM) Testing: Evaluating the flexibility and movement of the ankle and foot joints. Limited ROM can contribute to plantar fasciitis. A study in the *Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine* found that restricted ankle dorsiflexion is a risk factor for developing plantar fasciitis.
4. Strength Testing: Measuring the strength of the muscles in the foot and lower leg. Weakness in these muscles can lead to improper foot mechanics and increased stress on the plantar fascia.
5. Palpation: Physically examining the foot to pinpoint the exact location of pain and inflammation. This helps in differentiating plantar fasciitis from other causes of heel pain, such as heel spurs or stress fractures.
6. Functional Tests: Conducting activities that mimic daily movements to observe how the foot functions under stress. Functional testing can provide insights into specific activities that exacerbate the condition.
Treatment Options
Treatment for plantar fasciitis often involves a combination of approaches aimed at relieving pain, reducing inflammation, and correcting biomechanical issues. Key components of a physiotherapy-based treatment plan include:
1. Manual Therapy
Soft Tissue Mobilization: Techniques such as massage can help reduce tension in the plantar fascia and surrounding muscles. A systematic review in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy supports the use of manual therapy for pain relief and functional improvement in plantar fasciitis patients.
Joint Mobilization: Ensuring proper joint mechanics can alleviate stress on the plantar fascia.
2.Stretching Exercises
Plantar Fascia Stretching: Simple exercises, such as pulling the toes towards the shin, can stretch the plantar fascia and alleviate tension. A randomized controlled trial published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery found that plantar fascia-specific stretching is effective in reducing symptoms.
Calf Stretching: Tight calf muscles can increase strain on the plantar fascia. Stretching the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles can help.
3.Strengthening Exercises
Intrinsic Foot Muscles: Strengthening exercises for the small muscles within the foot can improve arch support. The Journal of Athletic Training highlights the importance of foot muscle strengthening in managing plantar fasciitis.
Extrinsic Foot Muscles: Strengthening the muscles of the lower leg, such as the tibialis anterior and posterior, can help maintain proper foot alignment.
4. Orthotics
Custom Insoles: Providing arch support and cushioning can redistribute pressure and reduce strain on the plantar fascia. A meta-analysis in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders found that orthotic devices significantly improve pain and function in plantar fasciitis patients.
Night Splints: These devices keep the foot in a dorsiflexed position overnight, which helps stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon.
5.Modalities
Ultrasound Therapy: Can reduce inflammation and promote tissue healing. A study in the Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation showed that ultrasound therapy can be beneficial in managing plantar fasciitis.
Iontophoresis: The use of electric current to deliver anti-inflammatory medications directly to the affected area.
6. Education and Footwear Advice
Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive shoes with adequate arch support and cushioning can prevent excessive strain on the plantar fascia. A review in the *Foot & Ankle Specialist* emphasizes the role of appropriate footwear in preventing and managing plantar fasciitis.
Activity Modification: Advising patients on how to modify their activities to reduce stress on the foot, such as avoiding prolonged standing or high-impact activities.
Evidence-Based Practices
According to a review published in *PubMed*, a combination of stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and orthotic devices is effective in managing plantar fasciitis. Additionally, a *Quora* discussion highlighted the importance of addressing biomechanical issues through a comprehensive physiotherapy program to achieve long-term relief from plantar fasciitis.
A systematic review in the *Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy* supports the efficacy of manual therapy, stretching, and strengthening exercises in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. The study found that these interventions, when combined, lead to significant improvements in pain and function.
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, but with a detailed biomechanical assessment and a tailored physiotherapy treatment plan, effective management and relief are achievable. Combining manual therapy, stretching and strengthening exercises, orthotics, and patient education ensures a holistic approach to treating this common condition.
It is crucial to seek an assessment from a qualified physiotherapist to accurately diagnose and treat plantar fasciitis. For personalized care, consider booking an appointment with a dedicated registered physiotherapist at West Calgary Physio & Massage(Book now).
References
1. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
2. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research
3. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine
4. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
5. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery
6. Journal of Athletic Training
7. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
8. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
9. Foot & Ankle Specialist
10. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
Note: Ensure to verify and access the latest research articles and discussions for the most accurate and up-to-date information.

Taffy Zambuko
Contact Me